A flap is a section of soft tissue outlined by a surgical incision. These are used to expand alveolar bone sever the periodontal ligament and.

Different Flap Designs Have No Impact On Periodontal Outcomes On Second Molars After Impacted Third Molar Extraction The Journal Of The American Dental Association
The type of flap used in surgery varies based on its purpose the particular surgery and the anatomical area of the surgical procedure.
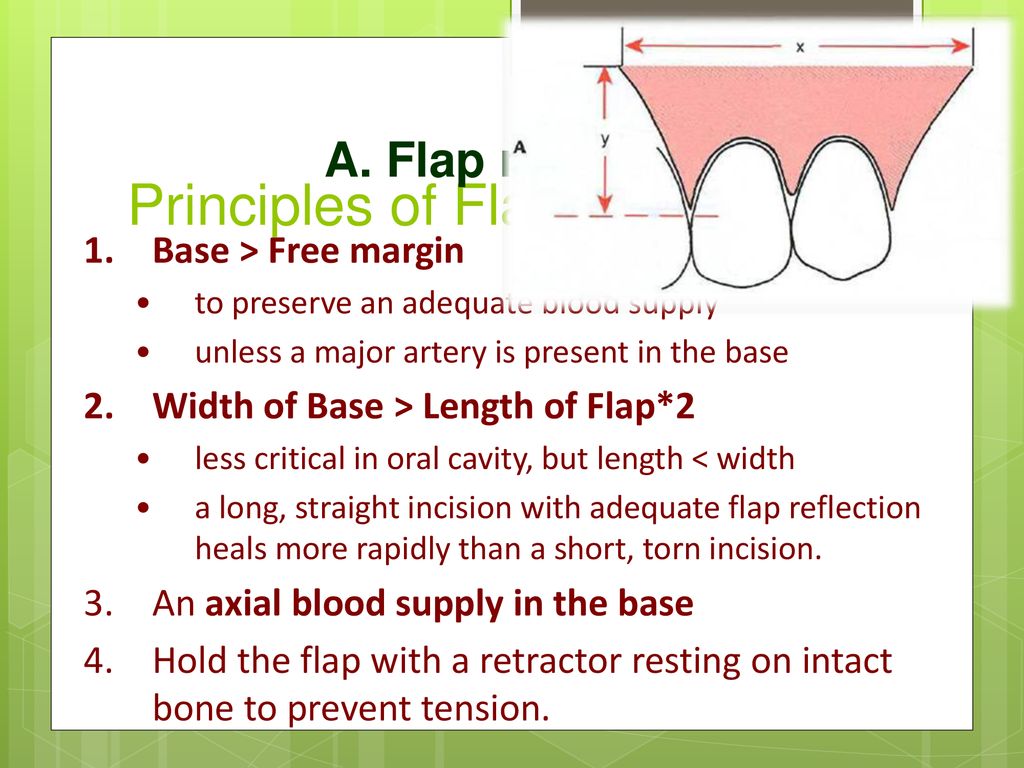
. Explain how flaps slats and airbrakes are used by an aircraft during landing. Must be maintained up to the point at bone. In general the flap should be based on maintaining blood supply and be broader at the base than at the apex Fig.
Principles of Flap Design and Closure - Oral Surgery - Jay B. The specific technique used to reconstruct a given facial defect should consider many basic principles. Oral surgery eature with specialized instruments and devices like proximators apical retention forceps and the piezotome.
The base wider than the apex. Learning Outcome 2 Understand how the stability and manoeuvrability of an aeroplane are controlled. Request PDF On Dec 31 2012 Andrew R.
The location and path of The lengthwidth ratio requirement Principle 4. Basic principle of flap design. Interested in flipbooks about Principles of Flap Design in Dental Implantology.
312 Acc ess Flap Principles of the MWFOcclusal View The surgical principles of the Ramfjord technique described above will be depicted here schematically from the occlusal view horizontal section. Flap blood perfusion must be maintained up to the point at which the ratio of length to the width of the parallel pedicle flap equals 21. The geometry of flap design and flap repositioning can be appreciated particularly well when viewed from the occlusal aspect.
Soft tissue flaps are frequently. The base of the flap must be broader than the free gingival margin to ensure adequate blood supply and to promote healing. Uncontrolled copy not subject to amendment.
View flipping ebook version of Principles of Flap Design in Dental Implantology published by on 2017-04-08. Flap design in dentoalveolar procedures varies depending on the procedure. The design for the flap should also facilitate wound closure once the surgical task is.
To understand flap design principles and anatomical considerations in planning a surgical extraction. Check more flip ebooks related to Principles of Flap Design in Dental Implantology of. Clinical questionlevel of evidence.
If papillae are involved. The submarginal and full mucoperiosteal incision will have either a three-corner ie triangular or four-corner ie rectangular design. The tissue flap must be kept moist at all times to help avoid.
Mucosa Connective tissue Periosteum. To be a successful designer a thorough knowledge and understanding of the basic principles of design is essential when designing Cronje 1996. Salama published Flap Classification and Principles of Flap Design for Head and Neck Reconstruction Find read and cite all the research you need on.
The flap itself must be larger than the bone deficit so that the flap margins when sutured are resting on intact healthy bone and not over missing or unhealthy bone thus preventing flap dehiscence and tearing. Reconstruction of deformities of the head and neck requires careful preoperative planning. To be able to design flaps for both the mandible and maxilla.
Therefore at most only a mini- Principle 8. A full-thickness mucoperiosteal flap includes the surface mucosa submucosa and the periosteum. To understand the technique required to make an incision and raise a flap in order to achieve better access for a surgical extraction.
It carries its own blood supply permits surgical access and when replaced and sutured is expected to heal by primary intention. Now that the main ways of classifying flaps have been introduced the remaining sections of this article are devoted to the most important principles to remember before performing flap surgery. The lengthwidth ratio requirement usually favors a slight trapezoidal shape of the flap3 Principle 13.
The number of teeth involved in the surgery The length and shape of the roots involved The. Flaps are necessary to facilitate surgical tooth removal treat pathology and create access for bone- and tissueaugmentation procedures. The flap should offer adequate access and have an adequate blood supply The flap must be of adequate size and fully reflected The edges must lie on the sound bone.
The flap should be wider than anticipitaed bony defect. Surgical Flap Design Considerations. Vertical releasing incision should start at buccal vestibule and end at the interdental.
Principles of Flap Design The incisions must be made over intact bone If the pathologic condition has eroded the buccocortical plate the incisionMissing. 2- Incision - the three most common incisions are 1Semilunar 2 submarginal 3 Sulcular. Principles of local flaps in head and neck reconstruction.
Like any surgical procedure flap surgery is not devoid of risk. Principles of flap surgery. The fundamental principles in surgical procedures include 1 flap preparation based on basic knowledge in vascularity of the involved tissues leading to appropriate flap designs papilla preservation avoidance of releasing incisions minimally-invasive techniques 2 flap mobilisation with respect to flap thickness and passive advancement and 3 flap.
Delicate handling of flap without tension. The basic principles of flap design should be followed. Basic principle of flap design Avoid anatomical structures The base wider than the apex Adequate width for maximum visualization The flap should be wider than anticipitaed bony defect Delicate handling of flap without tension Vertical releasing incision should start at buccal vestibule and end at the interdental papilla not at the buccal or labial surface.
Fundamental principles behind the vascular basis of the keystone flap and its modifications permit their greater utility in complex wounds in the settings of large oncologic resections irradiation and trauma. The term local flap indicates a section of soft tissue that 1 is outlined by a surgical incision 2 carries its own blood supply 3 allows surgical access to underlying tissues 4 can be replaced in the original position and 5 can be maintained with sutures and is expected to heal. Allow for proper iden- which the ratio of length to the width mal amount if any of the periosteum tification of important anatomical of the parallel pedicle flap equals 21.
Should be removed3 landmarks. Design principles are guides for using design elements Amenuke et al 1999. Request PDF On Jun 1 2012 Mohammed Jasim Al-Juboori and others published Principles of flap design in dental implantology Find read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate.
Share Principles of Flap Design in Dental Implantology everywhere for free. They are applied in situations where one wishes to create an attractive design for example as used in fashion styles. Many oral-surgery procedures require development of a surgical flap to gain access to the surgical site.
PRINCIPLE OF FLAP DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND MANAGEMENT. This should include precise analysis of the size and location of the defect. Complications such as complete flap loss can be catastrophic.
Adequate width for maximum visualization.
Principles Of Flap Design In Dental Implantology Flip Ebook Pages 1 8 Anyflip
Principles Of Flap Design In Dental Implantology Flip Ebook Pages 1 8 Anyflip

Periodontal Flap Surgery Ppt Download

Pdf Flap Techniques In Dentoalveolar Surgery

Pdf Principles Of Flap Design And Closure Oral Surgery Jay B Reznick Dmd Md


0 comments
Post a Comment